Unveiling Thrombosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
The circulatory system, a complex network of blood vessels, plays a vital role in sustaining life. However, certain conditions can disrupt this intricate balance, and one such concern is thrombosis—the formation of blood clots within the blood vessels. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures for thrombosis is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health.
The circulatory system, a complex network of blood vessels, plays a vital role in sustaining life. However, certain conditions can disrupt this intricate balance, and one such concern is thrombosis—the formation of blood clots within the blood vessels. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures for thrombosis is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health.
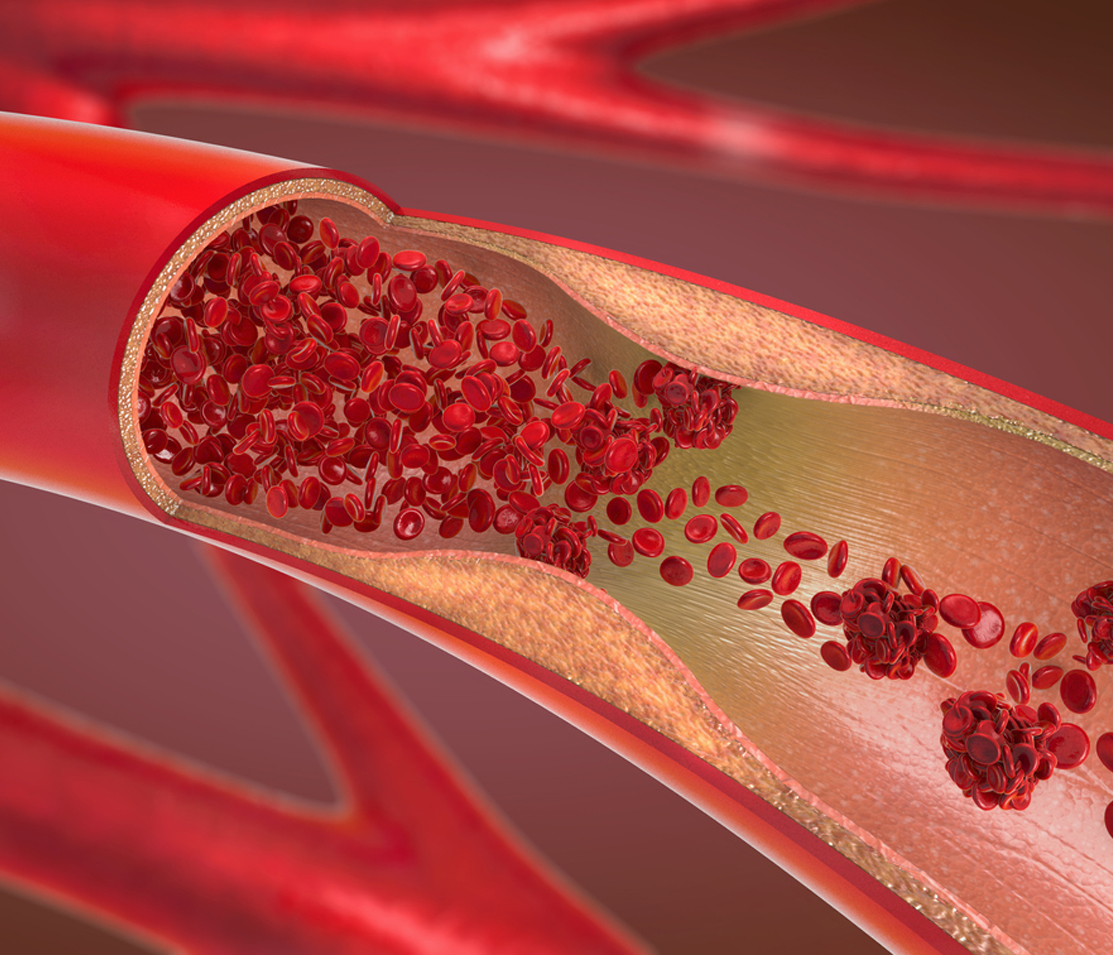
What is Thrombosis? Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot, or thrombus, forms within a blood vessel, disrupting the normal flow of blood. This condition can manifest in both arteries and veins, leading to various health complications depending on the location and size of the clot.
Causes of Thrombosis:
Hypercoagulability: Certain medical conditions and genetic factors can lead to an increased tendency of blood clot formation, a condition known as hypercoagulability.
Vascular Damage: Injury or damage to blood vessel walls can trigger the initiation of the clotting process, leading to thrombosis.
Stasis of Blood Flow: Conditions that cause sluggish or stagnant blood flow, such as prolonged immobility or congestive heart failure, can contribute to the formation of blood clots.
Symptoms of Thrombosis: The symptoms of thrombosis vary depending on the location of the clot.
Common signs include:
Swelling or pain in the affected limb: Thrombosis in the veins of the legs may cause pain, swelling, and redness.
Chest pain and shortness of breath: Thrombosis in the arteries supplying the heart or lungs can lead to chest pain and difficulty breathing.
Neurological symptoms: Clots in the brain can cause symptoms such as sudden severe headaches, vision changes, or weakness in one side of the body.
Stay Active: Regular physical activity promotes healthy blood flow and reduces the risk of blood clots. Simple activities like walking, jogging, or cycling can make a significant difference.
Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet that includes foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and fiber contributes to overall cardiovascular health and lowers the risk of thrombosis.
Hydration: Staying well-hydrated helps maintain the viscosity of blood, reducing the likelihood of clot formation.
Avoid Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for thrombosis. Quitting smoking not only benefits overall health but also lowers the risk of blood clot formation.
Manage Underlying Conditions: Effectively managing conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol reduces the risk of vascular damage and clot formation.
Medical Intervention: In some cases, individuals at a higher risk of thrombosis may be prescribed anticoagulant medications or antiplatelet drugs to prevent clot formation. It is crucial to follow medical advice and adhere to prescribed treatments.
Conclusion: Thrombosis is a serious condition that can have severe consequences if left untreated. By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can significantly lower their risk of developing blood clots and promote optimal cardiovascular health. A combination of a healthy lifestyle, regular medical check-ups, and awareness of risk factors empowers individuals to take control of their vascular well-being and enjoy a heart-healthy life.


Comments
Leave your comment